Office No. 608, Lunkad Sky Station, Viman Nagar Road, Pune, Maharashtra 411014, India
Phone: +1 213-261-0597
contact@techthinkmarketing.com
Does Google ads work Google Ads can be an effective advertising platform for many businesses when used strategically. Google Ads, formerly known as Google AdWords, is a pay-per-click (PPC) advertising platform that allows businesses to create and display ads on Google’s search engine and its partner network. Here are some key factors to consider regarding the effectiveness of Google Ads:

- Does Google ads work Targeted Advertising: Google Ads allows you to target your ads to specific keywords, geographic locations, demographics, and even user behavior. This level of targeting can help you reach a highly relevant audience.
- Cost Control: You have control over your budget and can set daily or monthly spending limits. This makes it accessible to both small and large businesses.
- Does Google ads work Measurable Results: Google Ads provides detailed performance metrics, allowing you to track clicks, impressions, conversions, and ROI. This data helps you measure the effectiveness of your campaigns and make adjustments as needed.
- Ad Formats: Google Ads offers various ad formats, including text ads, display ads, video ads, and more. This flexibility allows you to choose the format that best suits your business goals.
- Ad Extensions: You can enhance your ads with extensions that provide additional information, such as phone numbers, location details, links to specific pages on your website, and more.
- Competition: Depending on your industry and target keywords, competition in Google Ads can be fierce. The cost per click (CPC) can vary significantly, so it’s essential to manage your campaigns effectively to get a good return on investment (ROI).
- Quality Score: Google uses a Quality Score system to evaluate the relevance and quality of your ads and landing pages. Ads with higher Quality Scores are often rewarded with lower CPCs and better ad placements.
- Ad Campaign Management: Effective Google Ads management requires ongoing optimization and monitoring. This includes keyword research, ad copy testing, adjusting bids, and refining targeting.
It’s important to note that the success of Google Ads campaigns can vary widely depending on your industry, competition, and the quality of your ads and landing pages. Additionally, Google Ads is just one piece of a broader digital marketing strategy, and its effectiveness should be considered in the context of your overall marketing efforts.
Before investing in Google Ads, it’s advisable to conduct thorough research, set clear goals, and consider working with experienced professionals or agencies who can help you create and manage effective campaigns.
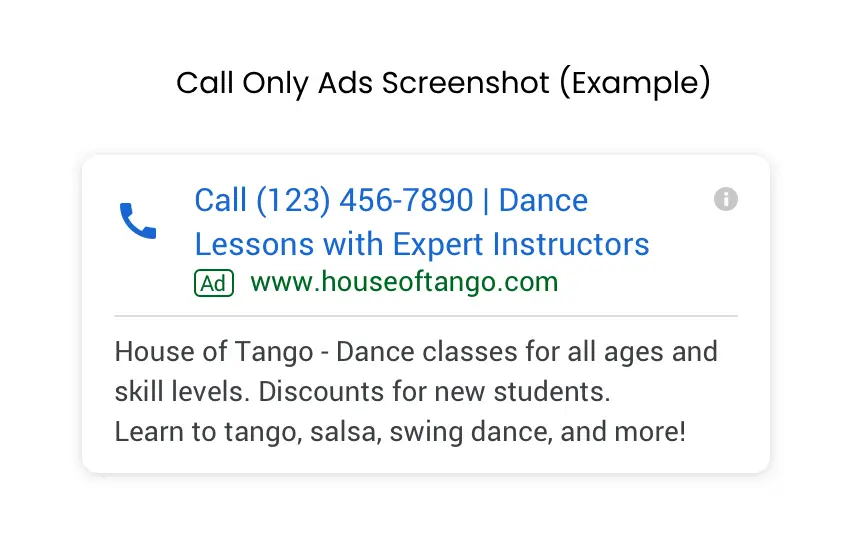
Table of Contents
ToggleType of Campaigns:
Does Google ads work businesses that are primarily offline can certainly leverage online marketing strategies to expand their reach and attract customers from all over the world. Here are some ways they can do this, as you’ve mentioned:
- Keyword Targeting: Does Google ads work Using targeted keywords in their online advertising and content can help businesses reach potential customers who are actively searching for their products or services. This can be done through search engine optimization (SEO) and pay-per-click advertising like Google Ads.
- Lead Generation Forms: Does Google ads work Online lead generation forms on a business website can capture contact information from potential customers. These forms can be used to gather leads for follow-up and conversion into paying customers.
- Call-Only Campaigns: Does Google ads work Call-only campaigns in platforms like Google Ads allow customers to directly call the business by clicking on the ad. This is especially useful for businesses that prefer phone inquiries or have complex products/services that require discussion.
- Address Directions Extensions: These extensions, often used in Google Ads, help customers find the physical location of a business. It’s particularly valuable for businesses like stores, cafes, and restaurants as it makes it easier for nearby customers to visit in person.
- Online Store: For retail businesses, setting up an e-commerce website can enable them to sell products to customers not just locally, but also globally. E-commerce platforms can reach a vast audience.
- Social Media: Does Google ads work Utilizing social media platforms can help businesses engage with a broader audience and promote their products or services. Social media can also be used for targeted advertising and building brand awareness.
- Content Marketing: Does Google ads work Creating valuable content related to the business’s industry or products can help attract a wider online audience. This can include blog posts, videos, and other forms of content that answer common questions or provide solutions.
- Local SEO: For businesses with physical locations, local search engine optimization is crucial. It helps them appear in local search results and maps, making it easier for local customers to find and visit them.
- Online Directories: Listing the business on online directories and review platforms can improve its visibility to potential customers and build credibility.
Does Google ads work It’s important for offline businesses to have a well-thought-out online marketing strategy, as competition online can be fierce. Additionally, tracking and analyzing the performance of online marketing efforts is crucial to ensure a positive return on investment (ROI). Businesses may consider working with digital marketing professionals or agencies to help them navigate the complexities of online marketing and maximize their reach and revenue.
Pricing models beyond pay-per-click (PPC)
Does Google ads work Does Google ads work Online advertising offers various pricing models beyond pay-per-click (PPC). Here are some common online advertising pricing models:
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC): In this model, advertisers pay a fee each time a user clicks on their ad. PPC is commonly used in search engine advertising (e.g., Google Ads) and display advertising.
- Pay-Per-Acquisition (PPA) or Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA): With this model, advertisers pay when a specific action is completed, such as a sale, lead generation form submission, or app download. Advertisers only pay when they acquire a customer or a specific conversion goal is met.
- Pay-Per-View (PPV): PPV advertising charges advertisers based on the number of times their ad is viewed or displayed, typically in the context of video advertising. It’s often used in video platforms like YouTube.
- Cost-Per-Mille (CPM): CPM is a pricing model where advertisers pay for every thousand impressions (views or displays) of their ad, regardless of whether users click on it. It’s commonly used in display advertising.
- Cost-Per-Engagement (CPE): This model charges advertisers when users engage with their ad in some way, such as expanding a rich media ad, watching a video ad for a specified duration, or interacting with an interactive ad format.
- Cost-Per-Action (CPA): Similar to CPA or PPA, this model charges advertisers when specific actions are taken, such as a form submission, app installation, or other predefined actions. It’s a broader term that encompasses various types of actions beyond just acquisitions.
- Cost-Per-Install (CPI): This model is often used in mobile app advertising, where advertisers pay for each app installation resulting from their ad campaign.
- Cost-Per-View (CPV): CPV advertising charges advertisers based on the number of video views, particularly in the context of online video advertising.
Does Google ads work The choice of pricing model depends on the specific advertising goals, industry, and platform. Each model offers its own advantages and challenges. Advertisers should consider factors such as the desired action, budget, and the target audience when selecting the appropriate pricing model for their online advertising campaigns.
Does Google ads work It’s worth noting that some platforms may offer a variety of pricing options, allowing advertisers to choose the one that best aligns with their objectives and budget. Advertisers should also closely monitor campaign performance to ensure they are achieving their desired results within their chosen pricing model.
Businesses across various industries can benefit using Google ads
Does Google ads work Google Ads can be beneficial for a wide range of businesses across various industries. The effectiveness of Google Ads often depends on the specific business goals, target audience, and the competitive landscape within a given industry. Here are some categories of businesses that commonly benefit from using Google Ads:
- E-commerce Stores: Does Google ads work Online retailers can use Google Ads to promote their products and drive sales. Google Shopping campaigns, in particular, are effective for showcasing products directly in search results.
- Local Businesses: Local businesses like restaurants, stores, service providers, and professionals can use Google Ads to target customers in their geographic area. Features like location extensions and Google My Business integration are valuable for local businesses.
- Professional Services: Lawyers, doctors, accountants, and other professionals can use Google Ads to attract clients searching for specific services in their area.
- Travel and Tourism: Airlines, hotels, tour operators, and travel agencies can use Google Ads to target travelers searching for flights, accommodations, and vacation packages.
- Education: Schools, colleges, and training institutions can use Google Ads to promote courses, workshops, and educational services.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and medical practices, can use Google Ads to attract patients searching for medical services or health information.
- Real Estate: Real estate agents and agencies can use Google Ads to showcase property listings and attract potential buyers or renters.
- Software and Technology: Companies offering software, apps, or tech solutions can use Google Ads to reach users searching for their specific products or services.
- Finance and Insurance: Financial institutions, insurance agencies, and investment firms can use Google Ads to target users interested in financial products and services.
- Home Improvement and Construction: Home renovation companies, contractors, and construction businesses can use Google Ads to connect with homeowners looking for remodeling or construction services.
- Event and Entertainment: Event organizers, concert venues, theaters, and entertainment businesses can use Google Ads to promote events and ticket sales.
- Automotive: Car dealerships, auto repair shops, and automotive parts stores can use Google Ads to target users searching for vehicles or automotive services.
- Online Services: Businesses offering online services such as web hosting, software as a service (SaaS), and digital marketing services can benefit from Google Ads to reach a global audience.
- Nonprofits: Nonprofit organizations can use Google Ads to raise awareness, promote fundraising campaigns, and attract volunteers.
- B2B Services: Business-to-business (B2B) companies can use Google Ads to generate leads and promote their services to other businesses.
Does Google ads work Keep in mind that the success of Google Ads campaigns depends on factors like budget, competition, ad quality, and effective targeting. It’s essential for businesses to conduct thorough research, set clear objectives, and continuously optimize their campaigns to maximize their return on investment (ROI) when using Google Ads.
Banner Ads:
Does Google ads work Display ads, also commonly referred to as banner ads, are a type of online advertising format that uses visual elements, such as images, graphics, and sometimes animation or multimedia content, to convey a message or promote a product or service. These ads are typically displayed on websites, social media platforms, apps, and other digital channels. Here are some key characteristics of display ads:
- Visual Elements:Does Google ads work Display ads are primarily visual in nature, often featuring eye-catching graphics, images, and sometimes videos. They are designed to grab the viewer’s attention.
- Standard Sizes: Display ads come in various standard sizes, such as 300×250 pixels (medium rectangle), 728×90 pixels (leaderboard), and 336×280 pixels (large rectangle), among others. These sizes are commonly used across the web.
- Placement: They can appear on websites, within apps, on social media platforms, and on ad networks. They can be placed in different positions on a web page, including above, below, or beside the main content.
- Targeting: Display ads can be highly targeted to specific demographics, interests, and behaviors of the intended audience. This precision targeting helps advertisers reach the right people with their message.
- Click-Through: Does Google ads work Display ads can be interactive and include call-to-action buttons or links that users can click to visit the advertiser’s website or landing page. Advertisers often pay for clicks (CPC) when users engage with the ad in this way.
- Cost: Advertisers can choose various pricing models for display ads, including cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-thousand-impressions (CPM), and cost-per-acquisition (CPA).
- Retargeting: Display ads are often used for retargeting campaigns, where ads are shown to users who have previously visited an advertiser’s website. This is a way to re-engage potential customers who may not have made a purchase initially.
- Ad Networks: Advertisers can utilize ad networks and programmatic advertising platforms to manage and distribute their display ads across a wide range of websites and apps.
- Rich Media: Some display ads incorporate rich media elements, such as video, audio, or interactive elements, to enhance user engagement and interactivity.
Does Google ads work Display ads can be an effective way to build brand awareness, promote products or services, and drive traffic to a website. However, their effectiveness depends on factors like ad design, targeting, relevance to the audience, and the quality of the landing page. Successful display ad campaigns often involve careful planning, testing, and optimization to achieve the desired results.
Search Ads
Does Google ads work Search engine advertising, often referred to as search engine marketing (SEM) or paid search advertising, is a form of online advertising that involves placing ads within search engine results pages (SERPs). Search engine ads are typically text-based and appear alongside or above the organic search results when users enter specific search queries. Here are some key aspects of search engine ads:
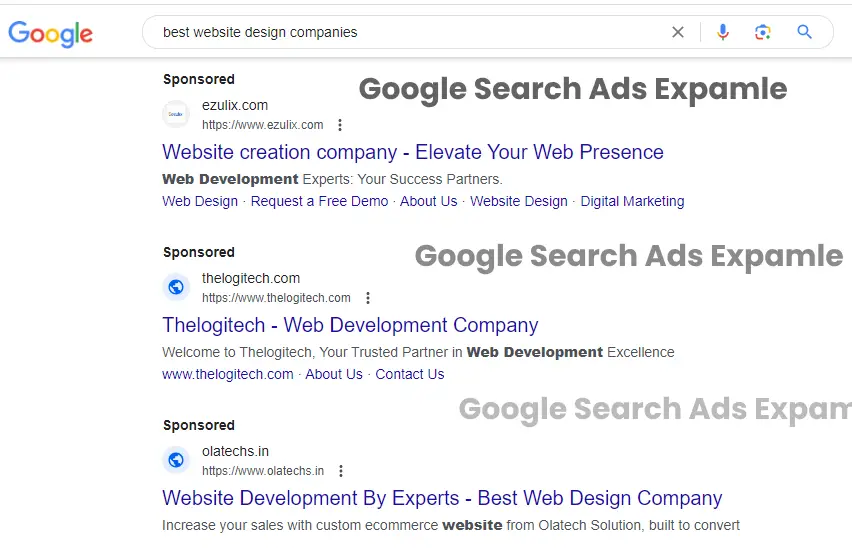
- Keyword Targeting: Does Google ads work Advertisers select specific keywords or phrases relevant to their products or services. When users search for these keywords, the ads are triggered to appear.
- Ad Auctions: Search engines like Google and Bing use auction systems to determine which ads to display for a given keyword search. Advertisers bid on keywords, and the search engine considers both bid amounts and ad quality to determine ad placements.
- Ad Copy: Search engine ads consist of text, including a headline, description, and display URL. Advertisers craft compelling ad copy to entice users to click on their ads.
- Ad Extensions: Advertisers can enhance their ads with ad extensions, which provide additional information, such as site links, callout extensions, location extensions, and more.
- Bid Strategies: Advertisers can choose from various bidding strategies, including manual bidding, automated bidding, and target CPA (cost per acquisition), to control their ad spend and optimize campaign performance.
- Budget Control: Advertisers set daily or monthly budgets to control their ad spend, and they can adjust budgets as needed.
- Quality Score: Search engines assess the quality of ads and landing pages through a metric called Quality Score. Higher-quality ads and landing pages often receive better ad placements and lower costs per click (CPC).
- Conversion Tracking: Does Google ads work Advertisers can track conversions, such as sales, leads, or other desired actions, to measure the effectiveness of their ad campaigns.
- Geographic Targeting: Does Google ads work Advertisers can specify the geographic locations where their ads should appear, allowing for local or global targeting.
- Mobile Ads: Search engine ads can be customized for mobile devices, ensuring a seamless experience for mobile users.
- Remarketing: Advertisers can use remarketing campaigns to target users who have previously visited their websites but did not convert. These ads aim to re-engage potential customers.
- Ad Schedule: Advertisers can schedule when their ads appear, allowing them to optimize ad delivery for specific days and times.
Does Google ads work Search engine advertising is effective for various business goals, including driving website traffic, increasing brand visibility, generating leads, and boosting e-commerce sales. It offers a high degree of control, precision targeting, and measurable results. However, successful search engine ad campaigns require ongoing management, optimization, and attention to detail to maximize return on investment (ROI). Google Ads and Microsoft Advertising (formerly Bing Ads) are among the most popular platforms for search engine advertising.





